- December 12, 2023
- Sathish Kumar
- 0 Comments
- 6546 Views
- 0 Likes
- Companies Act 2013
a ‘CIN’ of a Company can tell you Six Things
Do you deal with companies? Have you ever come across a alphanumeric 21 digit code called CIN? Whenever you will look at Company’s details, you would see a CIN i.e Company Identification Number. As the name suggests, every company that is incorporated in India is given a unique code at the time of its incorporation which is called the Corporate Identification Number (CIN) of that company.
This code is given irrespective of whether the company is a listed
company, private company, public company or One Person Company.
You can look for CIN of the companies in a corporate directory. CIN is also mentioned on the letter head of the company.
Can a Company’s CIN change?
Yes. CIN is the number with which you identify a company. Typically CIN is to remain with the company for a lifetime but in few cases, the CIN of the company may change:
- Change in State where registered office of the company is situated
- The listing status of the company changes
- The industry of the company changes
- The company becomes public limited from private limited or vice versa.
Breaking the CIN Code
CIN is not a random alphanumeric 21 digit code given to companies. It
infact, stores vital information in it. Let’s understand it by an
example:
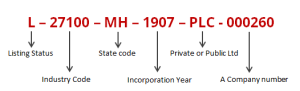
As shown above, the CIN Number is basically divided into 6 parts. Each part contains some information about the Company:
- First Digit represents the listing status – A Company may be either listed or unlisted. First Digit of the CIN indicates the Listing status
of the company. If the company is listed, It will be mentioned “L”, if
the company is unlisted, it will be mentioned “U” as the first digit of
the CIN. - Next Five Digits represents the Industry Code – Depending
on the business line chosen by the company, the Company selects an
industry in which it intends to operate. Accordingly, a suitable
industry code is allotted to the company. - Next Two Digits represents the State Code –
These digits represent the State in which the registered office of the
company is situated. Therefore, it helps us know which Registrar or ROC
is applicable with respect to the company.
For Example: If the company has been registered in Maharashtra, the Code
would be “MH”. In case, the company shifts its registered office to
some other place later, the CIN would change due to change in the State
Code. - Next Four Digits represents the year of incorporation of the Company –
These digits represents the year in which the company was incorporated.
By looking at the CIN of the company, one can tell that the year in
which the company was incorporated. - Next Three Digits represents the type of the company – These three digits specify the type of the company. A company may be any of the following:
– Public Limited Company (PLC)
– Private Limited Company (PTC)
– Government of India Company, Centre (GOI)
– One person Company (OPC)
– Company of State Government (SGC)
– Section 8 Company – Not for Profit (NPL) - Last Six Digits – These last digits define the ROC Registration Number
of the company. They are unique numbers given to every company at the
time of incorporation by the ROC in which they are registering. This
number depends on the ROC in which the company is registering and also
the Industry which has been allocated to it.
This is what the 21 digit CIN Code
comprises of. Next time you see CIN of a company, there would be many
things that you should be able to tell just by looking it










Leave a Comment